 |
 |
 |
 |
OLED Displays (Organic Light Emitting Diode) technology
|
 |
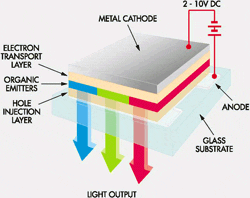
Principle and assembly of OLED displays
OLED displays are self-emitting displays, i.e. the display generates
its own light and is not dependent on background lighting.
The generation of light is reached by means of organic layers,
which are triggered to light by an electrical current, this
effect being known as electro-phosphorescence.
The organic layers consist of short-chained polymers (OLED)
or long-chained polymers (PLED).
|
 |
Advantages of OLED displays
- Thin construction, which is, at this point, defined by
the two glass plates. The light-emitting organic layers,
as well as the other additional layers, are only a few 100
µm.
- Very good viewing angle in all directions
- Good contrast
- Very high speed
- Wide range of temperature (-30°C to +80°C) and
no temperature dependence.
Disadvantages of OLED displays
- At present, only small displays (up to about 2.4")
are commercially available
- Storage life span (= half of the brightness) max. 60'000
h
- Limited functionality in sun light
OLED displays are available in monochrome versions (blue, yellow,
green, etc), in Area-Color versions or as Full-Color versions.
Area-Color display refers to displays which show a specific
color in one area, and in a second, another color. Typical application
in mobile phones, in which a status line, e.g. battery level,
signal strength, etc, is shown in one color, whilst the real
information is shown in a different color in a second area.
|
|
 |
|
 |

|
 |

Admatec AG
Fabrikstrasse 10
CH-4614 Hägendorf
Fon +41 62 896 00 48
Fax +41 62 896 25 80
info
|
|
 |




